Types Of Foundation And Where They Are Applicable
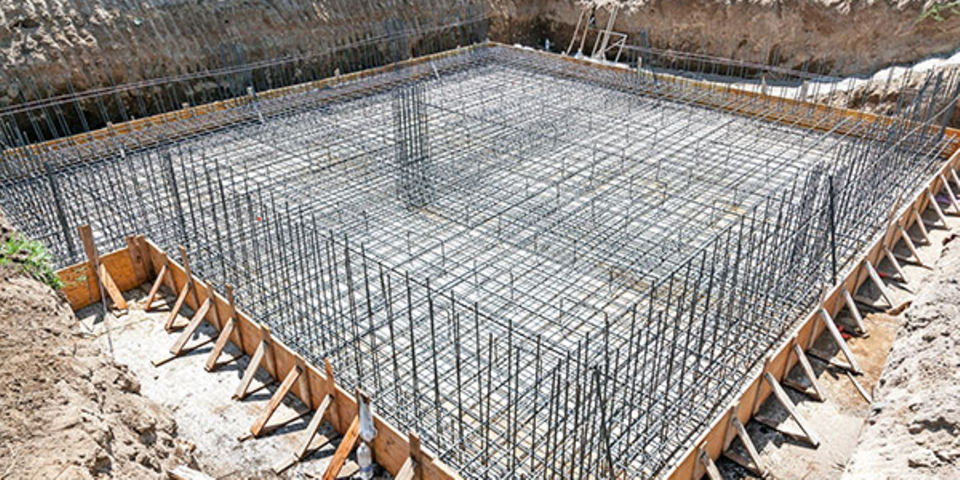
Foundations are essential to any construction project, providing a stable base for the building above. Several types of foundations are designed to suit specific soil and structural requirements.
The type of foundation used will depend on a range of factors, such as the soil type, the load-bearing capacity required, and the site's environmental conditions.
We will discuss the different types of foundations and where they are applicable to help you determine which foundation is best suited for your construction project. Foundations are generally grouped into two major categories.
- Shallow foundation
- Individual footing or isolated footing
- Combined footing
- Strip foundation
- Raft or mat foundation
- Deep Foundation
- Pile foundation
- Drilled Shafts or caissons
Shallow Foundation
Individual or isolated footing

This foundation supports a single column or load-bearing element. It is a square or rectangular-shaped foundation reinforced with steel bars and cast in place with concrete. Individual footings are ideal for small structures and are commonly used in residential construction.
Combined footing

A combined footing supports two or more columns that are close to each other. It is a single rectangular or trapezoidal footing reinforced with steel bars and cast in place with concrete. Combined footings are used when the individual footings overlap or interfere with each other.
Strip foundation

Strip foundations are long, narrow concrete footings that support a load-bearing wall or row of columns. They are typically used in buildings with a continuous load-bearing wall and can be reinforced with steel bars. Strip foundations are an economical solution for structures with a shallow soil depth.
Raft or mat foundation
A raft foundation, also known as a mat foundation, is a large, flat concrete slab used to support a heavy or complex structure.
It is reinforced with steel bars and extends over the entire footprint of the building. Raft foundations are used in buildings with high soil pressure or soft soil conditions, as they distribute the load evenly over a large area.
B. Deep Foundation
Pile foundation
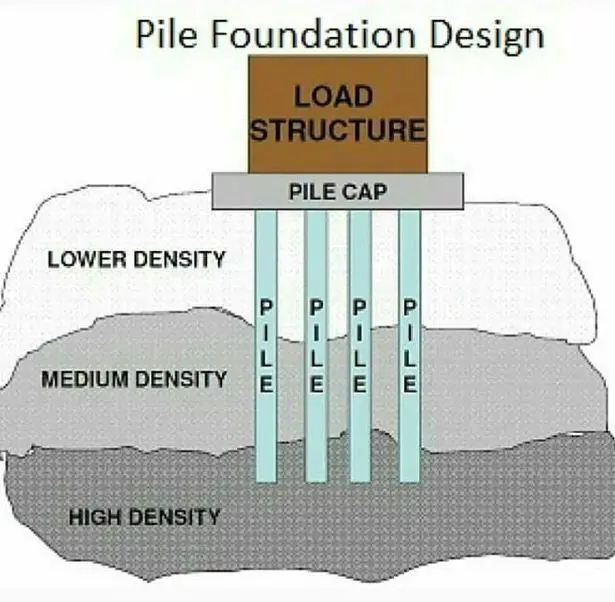
A pile foundation is a deep foundation used when the soil at the surface cannot support the weight of the structure. It consists of long, slender steel, concrete, or wood columns driven deep into the ground. Pile foundations transfer the structure's load to deeper, more stable soil layers, providing a strong and stable base.
Drilled Shafts or Caissons
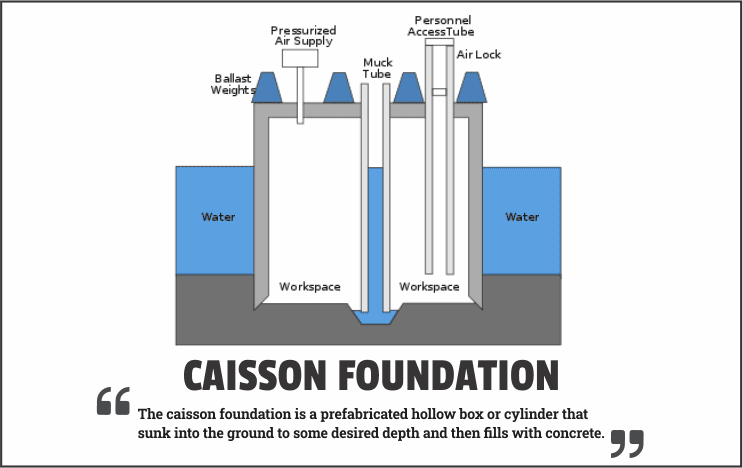
Drilled shafts, or caissons, are deep foundations similar to pile foundations. They consist of cylindrical shafts drilled into the ground and filled with concrete.
Drilled shafts are commonly used in bridge construction, high-rise buildings, and other structures with heavy loads.
They offer greater resistance to lateral forces than pile foundations and can be used in areas with high groundwater tables.





